What fungicides control Pythium root rot on creeping bentgrass greens the best?
In 2022, we conducted three Pythium root rot experiments at the North Carolina State University Turfgrass Field Lab in Raleigh, N.C., on ‘Dominant Plus’ creeping bentgrass, maintained as a golf course putting green with a root zone meeting USGA specifications (1,2,3).

Table 1 (Graphic: Golfdom Staff)
We mowed plots six times weekly at 0.150 inches and collected clippings. We fertilized the study with urea at a rate of 0.125 lbs. N per 1000 sq. ft. every other week.
We promoted Pythium root rot symptoms by irrigating the experiments three times daily for three minutes at 12:00 a.m., 5:00 a.m., and 5:00 p.m. starting in May and continuing through the end of July.
Individual plots were 3-by-6 feet and arranged in a randomized complete block design with four replications. We applied treatments in water equivalent to 2 gallons per 1000 sq. ft., with a CO2-powered sprayer equipped with a single AI9508E (TeeJet) nozzle at 50 psi. From there, we irrigated the plots immediately after application with 0.125 inches of water.
We started the treatment programs on June 1, 2022, and reapplied on June 15, June 30, July 27 and Aug. 11, 2022.
We visually assessed Pythium root rot symptoms as the percent area of the plot exhibiting symptoms on July 11 and 26 and Aug. 9, 2022. We did an analysis of variance for each experiment and separated means using Fisher’s Protected LSD test (P ≤ 0.05).
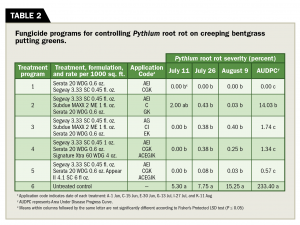
Table 2 (Graphic: Golfdom Staff)
Experiment 1
This experiment evaluated programs for the control of Pythium root rot (1). We first observed disease symptoms on July 11, with peak pressure occurring on Aug. 9 for the untreated controls averaging 15.25 percent Pythium root rot within the plots (Table 2). On July 26 and Aug. 9, all treatments provided excellent suppression of Pythium root rot compared to the untreated control.
All treatments significantly suppressed Pythium root rot throughout this trial when comparing AUDPC values (Table 2). However, treatment two had significantly more disease than treatments 1, 3, 4 and 5 compared to each other, yet still better than the untreated control.
Experiment 2
We evaluated Serata (FMC) alone and in tank mixtures for the preventative control of Pythium root rot on creeping bentgrass putting greens (2). The disease developed naturally in July.
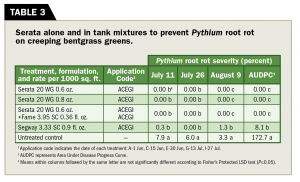
Table 3 (Graphic: Golfdom Staff)
Treatments containing Serata and Segway (PBI-Gordon) suppressed Pythium root rot preventively, regardless of application rate (Table 3). In comparison to Serata, Segway provided similar preventative control for Pythium root rot until Aug. 9.
All treatments suppressed Pythium root rot compared to the untreated control across all rating dates and when comparing AUDPC.
Experiment 3
In this last experiment, we evaluated Serata alone and in tank mixtures for the curative control of Pythium root rot on creeping bentgrass putting greens (3). The disease developed naturally at the end of June. However, disease severity was relatively minor, averaging about 3.8 percent in this trial (Table 4).
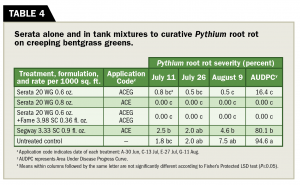
Table 4 (Graphic: Golfdom Staff)
Segway reduced Pythium root rot severity when compared to the untreated control, yet did not provide statistically similar suppression to Serata based on AUDPC values. Serata provided exceptional control of Pythium root rot regardless of rate or tank-mix partner on all rating dates and when comparing AUDPC.
In 2022, a similar trial conducted by researchers at the Pee Dee Research and Education Center at Clemson University provided similar results (4). Pythium root rot developed naturally across the experimental site in late June into early July. They observed disease progression resulting in uniform symptom development in late July and early August.
On July 7, Serata 0.6 fl. oz., Serata 0.4 fl. oz. + Fame 0.36 fl. oz., and Segway 0.67 fl. oz. all reduced Pythium root rot compared to the untreated control. During peak disease pressure on July 29 and Aug. 5, all treatments reduced Pythium root rot compared to the untreated control.
Their results show that Serata offers comparable control of Pythium root rot disease to Segway and that tank mixing at a lower rate of Serata (0.4 fl. oz.) with Fame SC 0.36 fl. oz. can provide comparable control to higher rates of Serata or Segway alone.